Hamster and Rabbit Difference – Hamsters.pk
Physical Characteristics: Size, Appearance, and Lifespan
When considering the differences between hamsters and rabbits, one of the most obvious distinctions lies in their physical characteristics. While both are small mammals commonly kept as pets, they have several unique features that set them apart. In this article, we will explore the differences in size, appearance, and lifespan between hamsters and rabbits.
Size
Hamsters are significantly smaller than rabbits. The average adult hamster typically weighs between 2 to 10 ounces (57 to 283 grams) and measures around 2 to 6 inches (5 to 15 cm) in length, depending on the specific breed. On the other hand, adult rabbits can weigh anywhere from 2 to 20 pounds (0.9 to 9 kg) and measure between 8 to 20 inches (20 to 51 cm) in length, again varying by breed.
Appearance
Hamsters and rabbits have distinct physical features that make them easily recognizable. Hamsters have short, stocky bodies with small, round ears and short, furry tails. They have large cheek pouches that they use to store and transport food. Hamsters come in a variety of colors and coat types, including short-haired and long-haired varieties.
Rabbits, in contrast, have elongated bodies with long, powerful hind legs adapted for hopping. They have prominent, upright ears that can grow quite large in some breeds. Rabbits have short, fluffy tails and do not have cheek pouches. They also come in a wide range of colors, patterns, and coat types, from short and smooth to long and fluffy.
Lifespan
Another notable difference between hamsters and rabbits is their lifespan. Hamsters have a relatively short lifespan, typically living between 2 to 3 years, although some may live up to 4 years with excellent care. This makes them a more short-term commitment as pets.
Rabbits, on the other hand, have a longer lifespan compared to hamsters. With proper care, domestic rabbits can live between 8 to 12 years, with some even reaching 15 years or more. This means that owning a rabbit is a longer-term commitment and requires careful consideration before bringing one home as a pet.
In conclusion, while hamsters and rabbits are both small mammals often kept as pets, they have distinct physical characteristics that set them apart. Hamsters are smaller in size, have short, stocky bodies, and have a shorter lifespan compared to rabbits. Rabbits are larger, have elongated bodies with powerful hind legs, and have a longer lifespan. Understanding these differences is crucial when deciding which pet is the best fit for your lifestyle and preferences.
Behavior and Temperament: Social Needs, Activity Levels, and Interaction with Humans

When considering the differences between hamsters and rabbits as pets, it’s essential to understand their behavior and temperament. This includes their social needs, activity levels, and how they interact with humans. In this article, we will explore these aspects in detail to help you determine which pet is better suited to your lifestyle and preferences.
Social Needs
Hamsters are solitary animals by nature and generally prefer to live alone. They can become territorial and aggressive towards other hamsters, especially if they are housed together in a small space. In some cases, dwarf hamster species may be kept in same-sex pairs or small groups if introduced at a young age, but this is not recommended for all breeds.
Rabbits, on the other hand, are social creatures that thrive on interaction with their own kind. In the wild, they live in groups called colonies. As pets, rabbits are happiest when kept in bonded pairs or small groups. They engage in social behaviors such as grooming, playing, and snuggling with their companions. Keeping a single rabbit can lead to feelings of loneliness and stress, which may result in behavioral issues.
Activity Levels
Hamsters are known for their high energy levels and love for exploration. They are most active during the evening and night, as they are crepuscular animals. Hamsters require ample space to run, burrow, and play, which can be provided through a large cage or enclosure equipped with toys, tunnels, and an exercise wheel.
Rabbits are also active animals but have different activity patterns compared to hamsters. They are most active during the early morning and late evening hours. Rabbits need plenty of space to hop, run, and play, as well as opportunities for mental stimulation. A spacious indoor enclosure or a rabbit-proofed room is ideal, along with supervised outdoor playtime in a secure area. Rabbits enjoy exploring, digging, and playing with toys such as cardboard boxes, tunnels, and willow balls.
Interaction with Humans
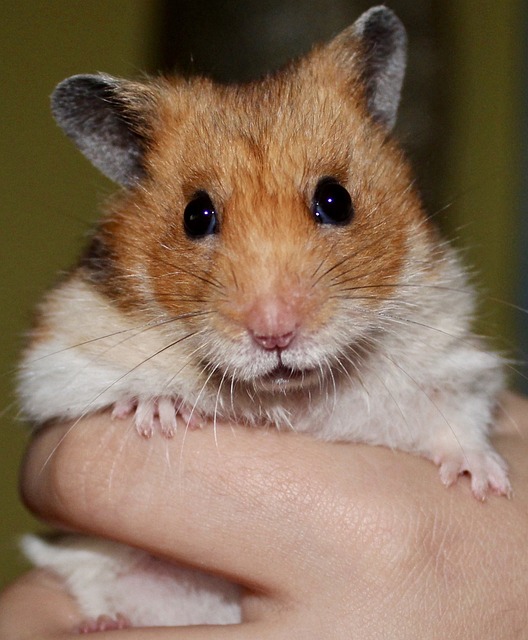
Hamsters can be friendly and interactive with their human companions, but they may require a more gradual approach to socialization. They can learn to enjoy gentle handling and may even climb into their owner’s hand for treats. However, some hamsters may nip if startled or frightened, so it’s crucial to handle them gently and respect their boundaries.
Rabbits, when properly socialized, can form strong bonds with their human caretakers. They are intelligent animals that can learn to respond to their names, follow simple commands, and even use a litter box. Many rabbits enjoy spending time with their owners, whether it’s snuggling on the couch, playing interactive games, or simply being petted. However, it’s important to remember that rabbits are prey animals and may become frightened or defensive if handled improperly.
In conclusion, hamsters and rabbits have different social needs, activity levels, and interactions with humans. Hamsters are solitary, high-energy animals that require ample space for exploration and play. Rabbits are social, active animals that thrive on interaction with their own kind and can form strong bonds with their human companions. Considering these differences will help you choose the pet that best suits your lifestyle and preferences.
Housing and Care Requirements: Enclosure Size, Diet, and Health Concerns
When bringing home a hamster or rabbit as a pet, it’s crucial to understand their specific housing and care requirements. This includes providing an appropriate enclosure size, a balanced diet, and being aware of potential health concerns. In this article, we will explore these aspects in detail to ensure that your pet lives a happy and healthy life.
Enclosure Size
Hamsters require a spacious cage or enclosure that allows them to engage in their natural behaviors, such as running, burrowing, and playing. A minimum cage size of 24 x 12 x 12 inches (60 x 30 x 30 cm) is recommended for most hamster species, with larger breeds needing even more space. The enclosure should include a solid floor, proper ventilation, and multiple levels or platforms for exploration.
Rabbits, being larger animals, need a more expansive living area compared to hamsters. A minimum enclosure size of 4 x 2 x 2 feet (120 x 60 x 60 cm) is recommended for a single rabbit, with an additional 2 square feet (0.2 square meters) added for each additional rabbit. The enclosure should have a solid, non-slip floor, proper ventilation, and ample space for the rabbit to hop, stretch out, and stand up on their hind legs without their ears touching the roof.
Diet
A balanced diet is essential for the health and well-being of both hamsters and rabbits. Hamsters are omnivores and require a diet consisting of high-quality hamster pellets, fresh vegetables, and occasional protein sources such as mealworms or crickets. They also need constant access to fresh, clean water. Avoid giving hamsters sugary or fatty treats in excess, as this can lead to obesity and other health issues.
Rabbits, on the other hand, are herbivores and have specific dietary needs. The bulk of their diet should consist of unlimited fresh hay, which aids in digestion and dental health. Additionally, rabbits should be offered a variety of fresh vegetables daily, along with a limited amount of high-quality rabbit pellets. Fresh, clean water should always be available. Avoid feeding rabbits foods high in carbohydrates or sugars, as their digestive systems are not designed to handle these types of food.
Health Concerns
Both hamsters and rabbits can be prone to certain health issues that owners should be aware of. Hamsters are susceptible to dental problems, such as overgrown teeth, which may require regular trimming. They can also develop digestive issues if fed an improper diet or if their living environment is unsanitary. Other health concerns include respiratory infections, skin problems, and tumors.
Rabbits are also prone to dental issues, as their teeth grow continuously throughout their lives. Regular dental check-ups and providing plenty of hay can help prevent overgrown teeth. Rabbits can also be susceptible to gastrointestinal stasis, a potentially life-threatening condition where the digestive system slows down or stops. Other health concerns include ear infections, skin problems, and urinary tract issues.
In conclusion, providing appropriate housing and care is essential for the health and happiness of both hamsters and rabbits. Hamsters need a spacious cage with ample room for exploration and a balanced diet consisting of pellets, vegetables, and occasional protein sources. Rabbits require a larger enclosure, an unlimited supply of fresh hay, a variety of vegetables, and a limited amount of pellets. Being aware of potential health concerns and providing regular veterinary check-ups can help ensure your pet lives a long and healthy life.
Suitability as Pets: Compatibility with Children, Other Pets, and Living Situations
When considering whether a hamster or rabbit is the right pet for your household, it’s important to evaluate their suitability based on various factors, such as compatibility with children, other pets, and your living situation. In this article, we will explore these aspects in detail to help you make an informed decision.
Compatibility with Children
Hamsters can make good pets for older children who understand the importance of gentle handling and respect for the animal’s needs. However, they may not be the best choice for very young children, as hamsters are delicate and can easily be injured if handled roughly. Hamsters can also bite if they feel threatened or frightened, which can be a concern for children who may not understand the animal’s body language.
Rabbits, when properly socialized, can be excellent pets for families with children. They are generally more tolerant of handling than hamsters and can form strong bonds with their human companions. However, it’s crucial to teach children how to interact with rabbits respectfully and to always supervise playtime to prevent accidental injury to the rabbit or child. Rabbits can also become stressed or frightened if handled improperly, so it’s important to educate children on the rabbit’s needs and body language.
Compatibility with Other Pets
Hamsters are solitary animals and should not be housed with other pets. They can become territorial and aggressive towards other animals, including other hamsters. It’s best to keep hamsters in a separate enclosure away from other household pets to prevent stress and potential injury.
Rabbits can be compatible with certain other pets, depending on the individual animal’s personality and socialization. Some rabbits can coexist peacefully with cats or dogs if introduced gradually and supervised closely. However, it’s essential to remember that rabbits are prey animals and can easily become frightened or stressed by predatory pets. Always ensure that your rabbit has a safe space to retreat to and never leave them unsupervised with other animals.
Living Situations
Hamsters are well-suited to smaller living spaces, such as apartments or homes with limited room for a pet. They require a relatively small enclosure and can be kept in a bedroom or dedicated pet area. However, it’s important to note that hamsters can be noisy at night due to their nocturnal nature, which may be a concern for light sleepers or those living in close quarters with neighbors.
Rabbits require a larger living space compared to hamsters, both for their enclosure and for supervised playtime. They need room to hop, stretch, and explore, which may be more challenging in smaller apartments or homes with limited floor space. Rabbits can also be destructive if not provided with appropriate toys and chew items, so it’s crucial to rabbit-proof your living area to prevent damage to furniture or electrical cords.
In conclusion, when assessing the suitability of hamsters and rabbits as pets, it’s important to consider their compatibility with children, other pets, and your living situation. Hamsters may be better suited for older children and smaller living spaces, while rabbits can be good companions for families with children and have more flexibility in terms of living arrangements. However, both pets require dedicated care, attention, and a commitment to meeting their specific needs to ensure a happy and healthy life.